-
Fruits
Banana
Origin
It is native to south of Asia. It was known in the Mediterranean since 650. It reached the Canary Islands in the 15th Century and from there it was taken to America in 1516. It began to be grown in the Canaries at the end of the 19th Century and beginning of the 20th Century.Family: Musaceae.
Species: Musa cavendishii (edible bananaS when raw) and M. paradisiaca (platains eaten cooked).Nutritional Value
It has a high energy value (1.1-2.7 kcal/100 g), and is a major source of vitamins B and C, like tomatoes and oranges. It contains numerous mineral salts, among them iron, phosphorus, potassium and calcium.The next chart shows the nutritional value of fresh bananas per 100 g of edible substance.
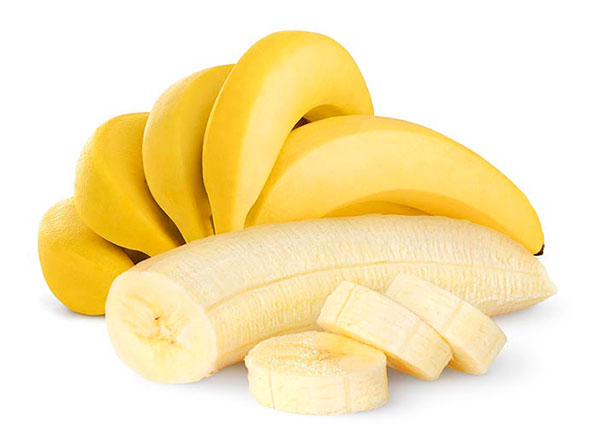

COMPONENTS VALUE COMPONENTS VALUE Water (g) 75.7 Proteins (g) 1.1 Lipids (g) 0.2 Carbohydrates (g) 22.2 Fibers (g) 0.6 Vitamin A (UI) 190 Vitamin B1 (mg) 0.05 Vitamin B2 (mg) 0.06 Vitamin B6(mg) (mg) 0.32 Nicotinic acid (mg) 0.6 Pantothenic acid (mg) 0.2 Malic acid (mg) (mg) 500 Citric acid (mg) 150 Oxalic acid (mg) 6.4 Sodium (mg) 1 Potassium (mg) 420 Calcium (mg) 8 Magnesium (mg) 31 Manganese (mg) 0.64 Iron (mg) 0.7 Copper (mg) 0.2 Match (mg) 28 Sulfur (mg) 12 Chlorine (mg) 125 Calories (kcal) 85
Mango
Origin
Mango is known today as one of the three or four finest tropical fruits. It was grown since prehistoric times. The Holy Scriptures in Sanskrit, Hindu legends and folklore of the year 2000 B.C. refer to this fruit as having an ancient origin, even then. The mango tree has been the object of great veneration in India and its fruits are highly valued as edible fruits throughout the ages.Apparently it is native from northeastern India and north of Burma in the slopes of the Himalaya; possibly also from Ceylon.
Botanical Classification
Mangifera indica L, is the most important member of the Anacardiaceae or the marañón family. Some of the well-know fruits of this family are, marañón (Anacardium occidentale L.), pistacchio (Pistacia vera L), mombins (Spondias spp.). The poisonous ivy or the poisonous oak of North America (Rhus toxicodendron L, or R.radicans L.) also belongs to this family, among other plants.Nutritional Value
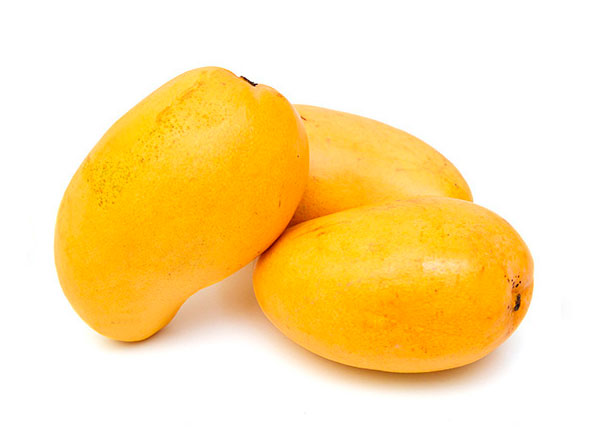

COMPONENTS VALUE COMPONENTS VALUE Water (g) 81.8 Carbohydrates (g) 16.4 Carbohydrates (g) 16.4 Fibers (g) 0.7 Vitamin A (U.I.) 1100 Proteins (g) 0.5 Ascorbic acid (mg) 80 Phosphorus (mg) 14 Calcium (mg) 10 Iron (mg) 0.4 Fats (mg) 0.1 Niacin (mg) 0.04 Thiamin (mg) 0.04 Riboflavin (mg) 0.07
Papaya
Origin
Central American (southern Mexico). It is currently grown in Florida, Hawaii, British Eastern Africa, South Africa, Ceylon, India, Canary Islands, Malaysian Archipelago and Australia.Botanical Classification
Family: Caricaceae
Order: Parietals
Species: Carica papayaNutritional Value
The next chart shows the nutritional value of fresh papaya per 150 g of edible substance.
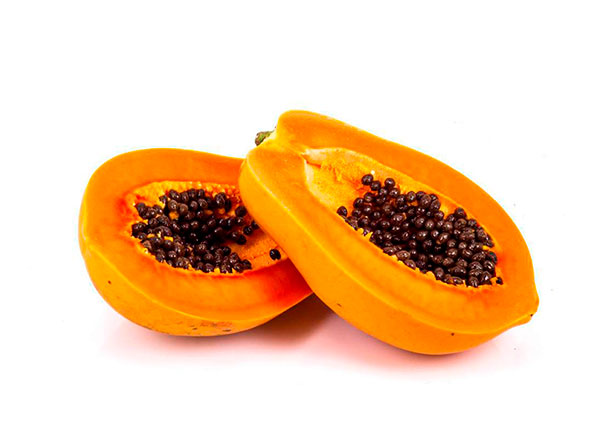

COMPONENTS VALUE COMPONENTS VALUE Water (g) 88.8 calories (kcal) 39 Fats s (g) 0.14 Carbohydrates (g) 8.81 Fibers g (g) 1.8 Potassium (mg) 257 Sodium (mg) 3 Phosphorus (mg) 5 Magnesium (mg) 10 Calcium (mg) 24 Vitamin C (mg) 61.8 Vitamin A (I.U.) 284 Vitamin B1 (mg) 0.027 Vitamin B2 (mg) 0.032 Niacin (mg) 0.338 Folic acid (mg) 38 -
DRY FRUITS
Peanuts
Origin
It is native from the tropical region of South America, probably Brazil. Even though some Asian countries, mainly China and India, produce nearly two thirds of the world crop, peanuts are today a major source of cooking oil in the American tropical region. In Africa, it comes in second place, next to palm oil.Botanical Classification
The peanut is a member of the pea family, of the Arachis genre. It is related to plants which include many species of major economic importance and many others that are used as ornament.Arachis hypogaea L. is an annual herbaceous, upright, climbing plant 15-70 cm tall with slightly furry stems, with ramifications from the base that grows roots when such branches touch the ground.
Nutritional Value
The fresh grains contain from 32 to 35% proteins, and from 40-50% fats plus cysteine, thiamin, riboflavin and niacin. They have a highly nutritious value and so play an important role in the diet of millions of people who cannot afford animal proteins and fats.
Nuts
Origin
The fruit is native of Persia (Himalaya region), according to some authors, or of China and Japan, according to others. It was taken to Greece and then to Italy and from there on to other European countries.There is fossil evidence of the presence of the Nogal J. regia in the Iberian Peninsula, going back to the Paleolithic.
The walnut tree lies in wild state in Eastern Europe and Asia Minor, also in North America; there are a number of species of this tree more or less cultivated.
The generic name comes from the Latin Juglans, Roman name for the tree and the nut, an abbreviation of lovis glans: Jupiter's acorn, and to its Latin version of the Greek God Balanos, name of the walnut and the chestnut, which literally meant: Zeuz's acorn or chestnut.
Botanical Classification
Family: Juglandaceae.
Genre: Juglans
Grown species: Juglans regia (European walnut), Juglans cinerea (cinder walnut), Juglans nigra (black walnut ), Juglans californica (California walnut).
Plant: Vigorous tree 24 - 27 m high; its trunk may reach up to 3-5 m diameter, with a leafy, large crown, in a compressed spherical form. Straight trunk, covered with a cindery thick bark, young branches are smooth and dark red and the old branches are brownish and cracked.Nutritional Value
Walnut is a fruit with some of the higher contents of iron, and easy to assimilate due to its contents of Vitamin C.
COMPONENTS VALUE COMPONENTS VALUE Lipids (%) 66 Proteins (%) 18 Potassium (mg) 500 Phosphorus (mg) 350 Calcium (mg) 100 Sodium (mg) 3 Iron (mg) 3 Calories (kcal) 678 -
VEGETABLES
Carrot
Origin
The carrot is a species native to central Asia and the Mediterranean. He has since been cultivated and consumed by ancient Greeks and Romans. During the early years of his crop, the roots of the carrots were purple in color.
The carrot is a species native to the center of them to change their current orange color is due to the selections that occurred in mid 1700 in Holland, which provided a large amount of carotene, the pigment that causes color and have been the base material current plantBotanical Classification
Family: Umbelliferae.
Scientific name: Daucus carota L.
Plant: Biannual. During the first year will form a little rosette of leaves and root. After a rest period, a short stalk in which the flowers are formed during the second growing season.Nutritional Value
The nutritional qualities of carrots are important, especially for its high content of beta-carotene (a precursor of vitamin A) because each molecule of which is consumed carotene is converted into two molecules of vitamin A. It is generally characterized by a high water content and low in fat and protein.Nutritional value of the carrot in 100 g of edible substance.

COMPONENTS VALUE COMPONENTS VALUE Water (g) 88.6 Carbohydrates (g) 10.1 Lipids (g) 0.2 Calories (cal) 40 Vitamin A (U.I.) 2.0-12.0 Vitamin B1 (mg) 0.13 Vitamin B2 (mg) 0.06 Vitamin B6 (mg) 0.19 Vitamin E (mg) 0.45 Nicotinic acid (mg) 0.64 Potassium (mg) 0.1
Radishes
Origin
The Origin of radishes has not been conclusively determined, although it appears that the varieties of radishes small originated in the Mediterranean region, while the large radishes could originate in Japan or China.
In inscriptions found in Egyptian pyramids, dated 2000 years BC, and referred to his cooking.Botanical Classification
Family: Cruciferae.
Scientific name: Raphanus sativus L.
Plant: anual o bienal.Nutritional Value
nutritional value of Radishes 100 g of fresh field
COMPONENTS VALUE COMPONENTS VALUE Carbohydrates (g) 2.44 Protides (g) 0.86 Vitamin A (U.I.) 30 Vitamin B1 (mg) 30 Vitamin B2 (mg) 20 Vitamin C (mg) 24 Calcium (mg) 37 Phosphorus (mg) 31 Iron (mg) 1
Cabbage
Origin
The cabbage is originally from the Far East, are cultivated in China for many years, where he arrived in Japan in the late nineteenth century. A pricipos century was widespread in Europe and America.Botanical Classification
The cabbage is originally from the Far East, are cultivated on cabbage belongs to the family Cruciferae. Its botanical name is Brassica campestris L. sp. pekinensis.Nutritional Value
Nutritional value of cabbage in 100 g of fresh field
COMPONENTS VALUE COMPONENTS VALUE Water (%) 95 Proteins (g) 1.2 Fats (g) 0.8 Carbohydrates (g) 3 Fibers (g) 0.6 Ashes (g) 0.7 Calcium (mg) 43 Phosphorus (mg) 40 Iron (mg) 0.6 Sodium (mg) 23 Potassium (mg) 253 Vitamin A 150 Thiamine (mg) 0.05 Riboflavin (mg) 0.04 Niacin (mg) 0.26 Ascorbic acid (mg) 25 -
FODDER
Alfalfa
Origin
Alfalfa originally comes from Asia Minor and south of the Caucasus, in countries like Turkey, Iraq, Iran, Syria, Afghanistan and Pakistan.The Persians introduced Alfalfa into Greece and from there it was passed on to Italy in the 4th Century B.C.
The widespread cultivation of this seed by the Arabs was extended across northern Africa. Once it reached Spain it was spread throughout Europe.
Botanical Classification
Alfalfa belongs to the family of leguminous plants; its scientific name is Medicago sativa. It is a perennial plant, vigorous and upright.Nutritional Value
The importance of the alfalfa crop lies in its being a natural source of protein, fiber, vitamins and minerals, as well as in its contribution to landscape and its use as a crop that helps in the preservation of fauna. Furthermore, it helps reduce the energy required to fix symbiosis of nitrogen for its own cultivation and for the next crops in their sequence of rotation of the group it forms part.
Since it is a perennial, meadow species, growing it provides interesting elements because it can be used to limit and reduce soil erosion and control certain pests and diseases of the crops that follow in the rotation sequence.
Celery
Origin
The celery plant comes from the Mediterranean, and other secondary areas such as the Caucasus and the Himalaya region. It was know in ancient Egypt. Its use as garden produce was developed in the Middle Ages and is currently consumed both in Europe and in North America.Botanical Classification
Celery belongs to the family of Umbeliferae. There are two botanical varieties: Apium graveolens var. dulce and Apium graveolens var. rapaceum; the latter known as celeriac or celery root. It has a strong taproot that grows deep into the ground, with superficial secondary roots. Stems 12 to 31 inches long grow from the neck of the root.Nutritional Value
Nutritional value of 100 g of fresh celery: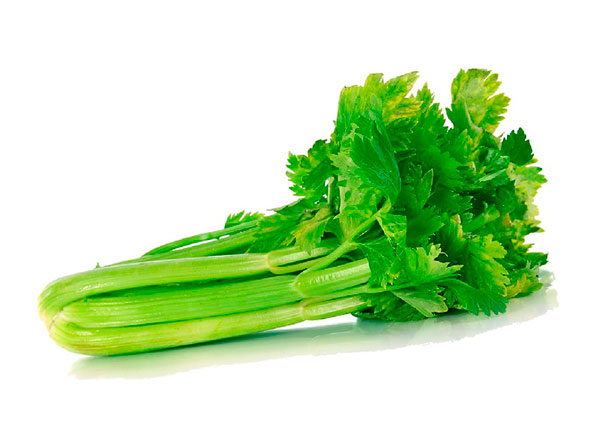
COMPONENTS VALUE COMPONENTS VALUE Calories (cal) 17 Water (%) 92 Proteins (g) 2 Carbohydrates (g) 1 Sodium (mg) 110 Potassium (mg) 300 Calcium (mg) 40 Vitamin C (mg) 12
Spinach
Origin
Spinach was introduced to Europe around the year 1000 from Asia, probably Persia, but only as of the 18th Century did it begin to spread throughout Europe, when exploitation of the crop began, mainly in the Netherlands, England and France. After that it was cultivated in other countries and much later it in America.Botanical Classification
Family: Chenopodiaceae.
Species: Spinacea oleracea L.
Plant: In the first phase it forms a rosette with leaves of variable duration according to climatic conditions; later it grows a stem. From the auxiliary buds or directly from the neck grow lateral stems that create secondary ramifications, and these can give flowers. There are masculine, feminine and even hermaphrodite plants that are easy to tell apart, since the feminine plants have a larger number of basal leaves, that are slow to bolt seeds and are therefore more productive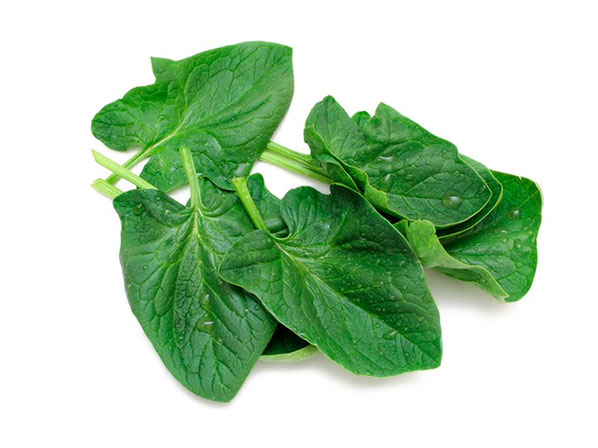
-
SEEDS
Girasol
Origin
The Origin of sunflowers dating back to 3,000 BC in northern Mexico and western United States, since it was cultivated by the indigenous tribes of New Mexico and Arizona. The sunflower was one of the major agricultural products used in food for many American communities before the discovery. Sunflower seed was introduced in Spain by the colonizers and then spread to the rest of Europe.
The sunflower has been cultivated for more than two centuries in Spain and elsewhere in Europe for its ornamental VALUE because of the size and especially the beauty of their heads
It was during the nineteenth century when the industrial exploitation of its oil for food..Botanical Classification
She belongs to the Asteraceae family, whose scientific name is Helianthus annuus. This is an annual plant, with a vigorous development in all its organs. Within this species or subspecies there are many types grown as ornamental plants, oil seeds and fodder..Nutritional Value
Sunflower seed is a source of calories Fats, in addition to Proteins and carbohydrates. The feeding of poultry soya meal only replacing part of sunflower meal, because its lysine content is lower. The shells left after oil extraction and milling can be used as an ingredient in the rations of ruminants. The fodder yeast is obtained from the husks and is a valuable protein feed for livestock and poultry. The heads of sunflower are used in feed for sheep and cattle, and the flour with these heads serve as a ration to the adult cattle and poultry. The sunflower is also a good honey plant.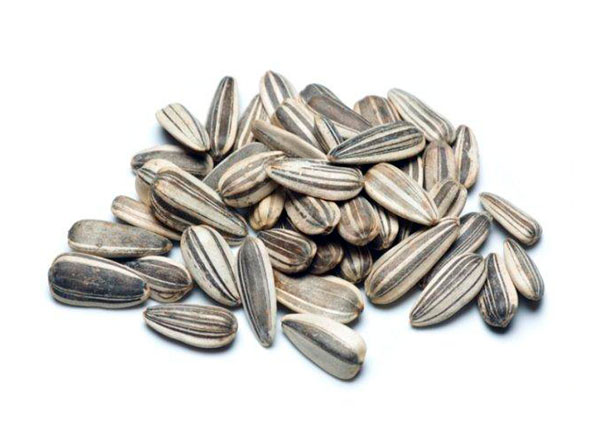
CORN
Origin
The corn crop is a very remote about 7000 years old, of Indian Origin under cultivation in the areas of Mexico and Central America. Today, its cultivation is very blurred by all the other countries and especially in Europe where he has a very high level. USA is another country that stands out for its high concentration in the cultivation of maize. His Origin is unclear but is believed to belong to a growing area of Mexico, as its oldest finds were found there.Botanical Classification
Common name: Corn
Scientific name: Zea mays
Family: Gramíneas
Genre: Zea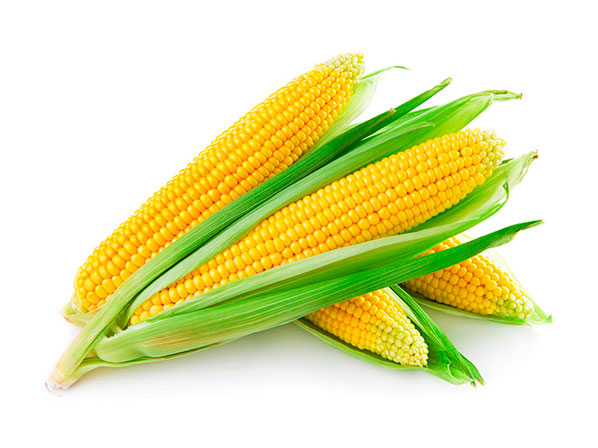
-
FOOD SUPPLEMENTS
- Vitafor A
Nutritional Value - Vitafor C
Nutritional Value - Necton A
Nutritional Value - Necton E
Nutritional Value - Fervinac con selenio
Nutritional Value - Magnafoscal
Nutritional Value
- Vitafor A
Nancy Fuentes
Phone: (52.55) 21673063
eMail:
This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
Mr. Fidel García
Phone: 01 (7773) 18-8973
eMail:
This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.